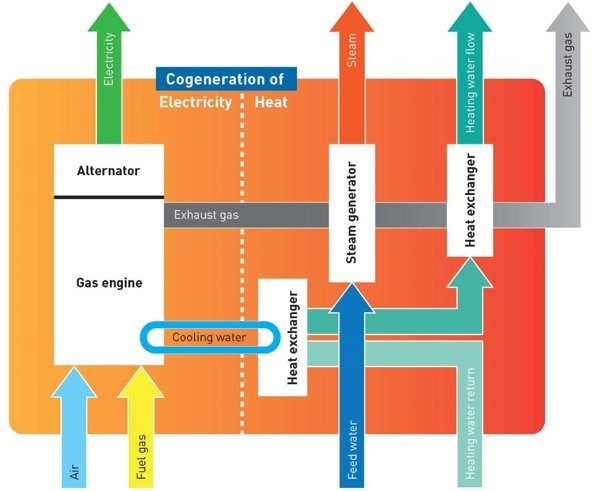
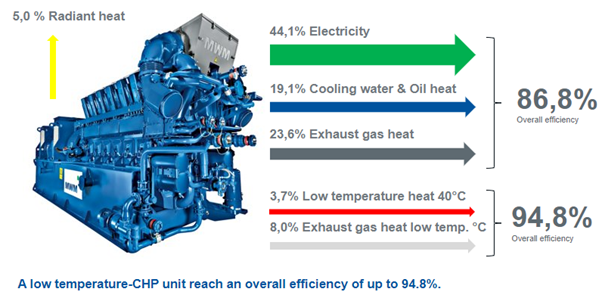
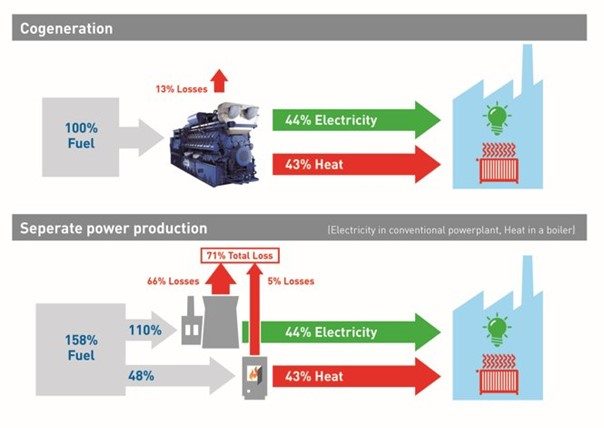
Cogeneration: A method of energy production that generates both electricity and heat within a single system.
Cogeneration System: A system that performs the cogeneration process.
Primary Energy Source: The fuel used in a cogeneration system (natural gas, biomass, coal, etc.).
Thermal Engine: An engine that converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy.
Generator: A device that converts mechanical energy into electricity.
Heat Recovery System: A system that makes waste heat from the thermal engine useful.
Heating: The process of meeting the heat requirements of buildings and processes.
Cooling: The process of meeting the cooling requirements of buildings and processes.
Efficiency: A measure of how effectively a system converts input into output.
Greenhouse Gas Emission: The release of gases into the atmosphere that cause climate change.
Energy Savings: Doing the same work using less energy.
Cost Savings: Saving money through energy savings.
Return on Investment (ROI): The profit gained from an investment.
Payback Period: The time it takes to recover the cost of an investment.
Government Incentives: Incentives provided by the government to businesses that invest in cogeneration systems.